OkHttpClient 应该被设计为一个单例,以便复用连接池与线程池,避免造成资源不必要的资源浪费
okhttp 的连接池设计
为了避免在请求同一个连接时在重新建立连接上产生的时延,Okhttp设计了socket连接 复用机制。
每次有新的请求到来时,会先去连接池中查找当前请求的连接是否已经存在。
如果连接存在(连接相同的标准是:),直接复用。
如果不存在,则重新创建一个连接,然后将连接放进连接池,在放进连接池时会通过
线程池对连接池进行清理与维护,用来释放已经空闲超时的连接.
okhttp 的连接池的清理逻辑
直接上源码
如果连接池中不存在当前请求的连接,则先判断当前连接池是否在执行清理操作,如果没有先执行连接池清理操作。然后将新的请求添加到连接池中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8void put(RealConnection connection) {
assert (Thread.holdsLock(this));
if (!cleanupRunning) { //如果不是是在清理中,则执行清理操作
cleanupRunning = true;
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable); //有线程池管理,执行清理操作
}
connections.add(connection);//添加连接到线程池
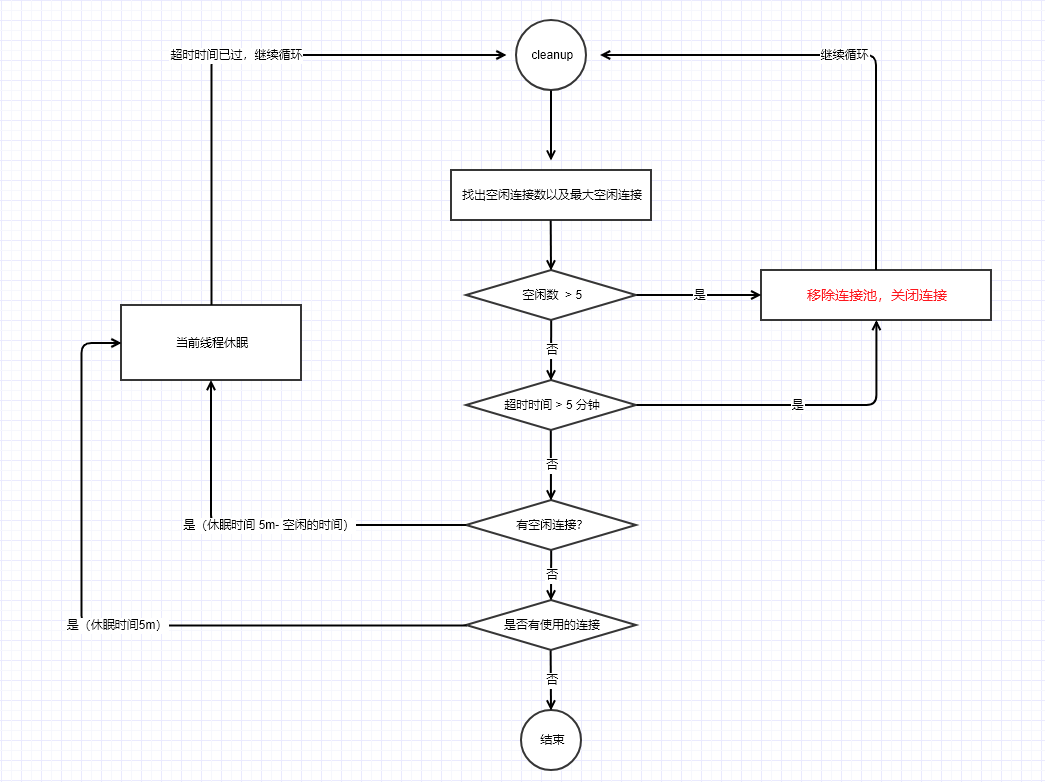
}执行清理操作,这里要注意两点:如果清理返回的结果为 -1,那么表示连接池中没有连接,那么清理线程也就没有一直循环下去的必要了。如果在清理的过程中发现有空闲连接,但是空闲连接没有达到超时时间,那么当前执行清理的线程会休眠(时间为达到超时的时间),如果在此休眠期间没有重新调用该连接,那么超时时间之后会执行清理操作。
1 | private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() { |
3.清理操作主要由cleanup执行,clean的时候分以下几个步骤:
1.首先先找到连接池中空闲时间最长的连接,以及空闲连接数
2.其次判断当前空闲连接数如果大于默认的连接数,则直接移除当前的空闲连接,关闭连接sokect
3.如果当前空闲时间大于默认的空闲时间,也直接移除当前的空闲连接,关闭连接sokect
4.如果当前连接池中存在空闲连接,那么直接返回超时时间差,返回之后,当前线程会休眠当前这个时间差,然后继续下一次清理
5.如果没有空闲线程,直接返回默认的超时时间,当前清理线程会休眠
6.如果没有连接,则当前清理线程会退出。
1 | long cleanup(long now) { |
来一张连接池的流程图:(为什么是5,默认超时时间是 5分钟,空闲链接为5,可以自定义)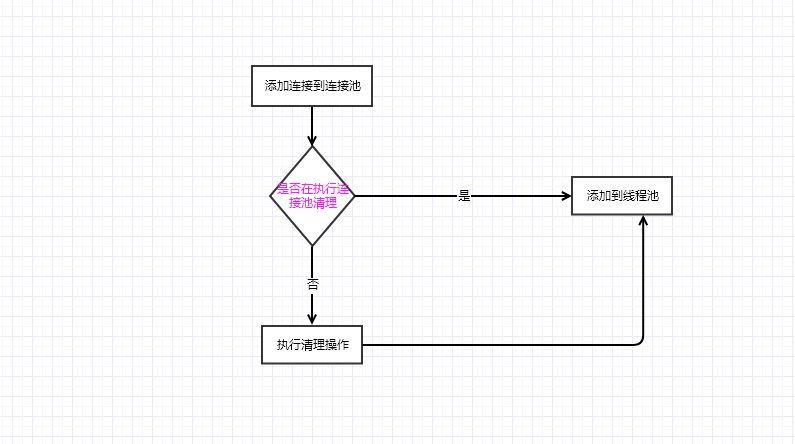
okhttp 的Cache设计
数据结构:private final Deque
完美的邂逅,这个纯属扯淡